Monday, 26 October 2020
Behaviour as a control loop located outside the organism
 With his famous Chinese Room Argument, philosopher John Searl raised an important question: can a computer understand Chinese (or French or English)? Probably not, if the results of some of today’s computer-translation programs are any indication. Unlike computers, we human beings can usually grasp the meaning of things fairly effortlessly, while a computer cannot. Many neuroscientists believe that to explain why, we must look more closely at the biological substrate of the brain, and in particular its long evolutionary history. (more…)
With his famous Chinese Room Argument, philosopher John Searl raised an important question: can a computer understand Chinese (or French or English)? Probably not, if the results of some of today’s computer-translation programs are any indication. Unlike computers, we human beings can usually grasp the meaning of things fairly effortlessly, while a computer cannot. Many neuroscientists believe that to explain why, we must look more closely at the biological substrate of the brain, and in particular its long evolutionary history. (more…)
Uncategorized | Comments Closed
Tuesday, 13 October 2020
Our perceptions are shaped by the possibility of imminent actions
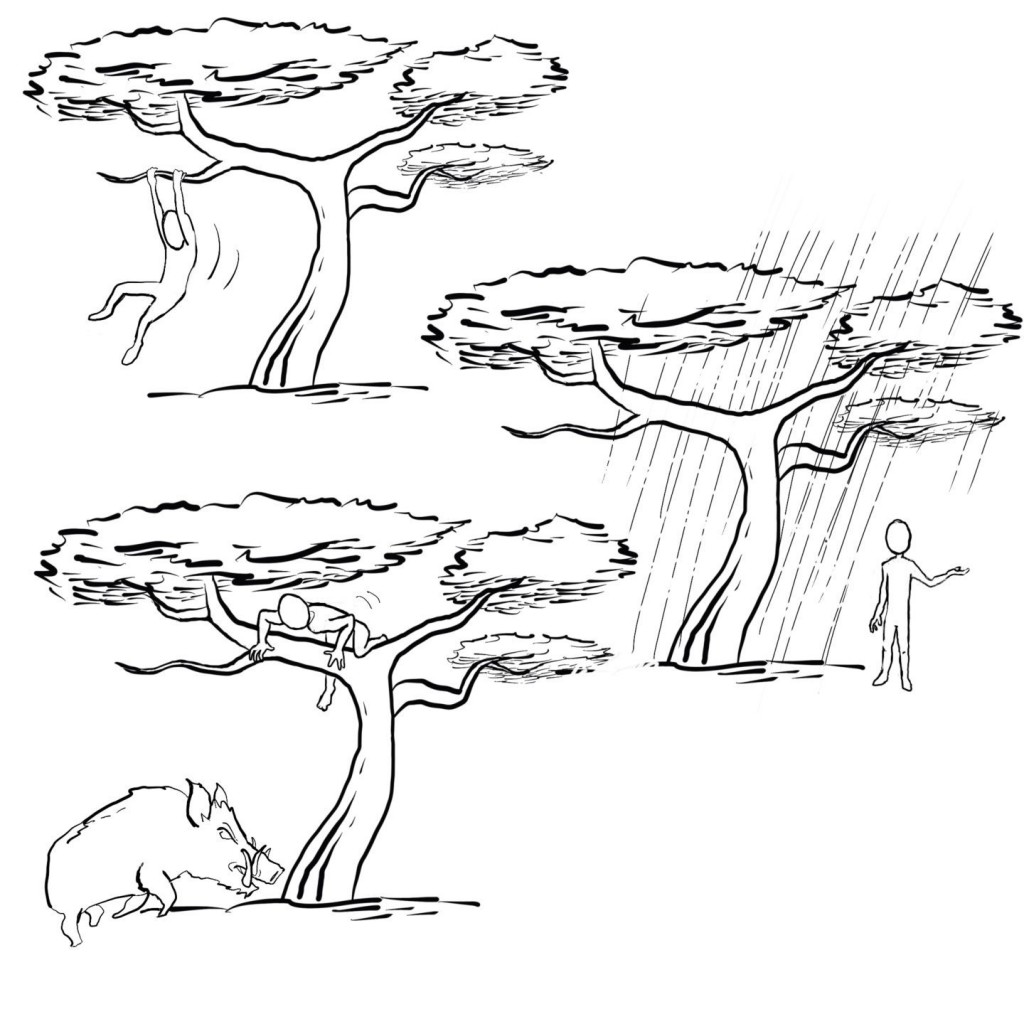
Affordances are a key concept in cognitive science, first advanced by J.J. Gibson in 1966. As I explained in an earlier post in this blog, an affordance is an opportunity that an object offers to take action. A hammer, for example, offers the opportunity to be grasped by its handle, and a chair offers the opportunity to sit down. What is interesting about this concept of affordances is that the opportunity for action does not depend on an object’s characteristics in any absolute sense, but instead is relative: it depends on the possible relationships that a particular organism may establish with that object. A tree, for example, offers different affordances to humans, who may use it as shelter from the rain, or crows, which may use it as a perch, or to woodpeckers, which may use it as a place to hunt for food. Moreover, as the above illustration suggests, any given object (again, such as a tree), may inspire different affordances for a given organism (such as a human) depending on that organism’s motivations and/or the broader general situation. (more…)
Body Movement and the Brain | Comments Closed







